Compression socks are specially designed garments that apply graduated pressure to your lower legs, improving circulation and reducing common leg problems like swelling, fatigue, and pain. Once primarily medical devices, they’ve evolved into mainstream wellness accessories embraced by athletes, travelers, healthcare workers, and anyone seeking better leg health.
What Do Different Types of Compression Socks Do?


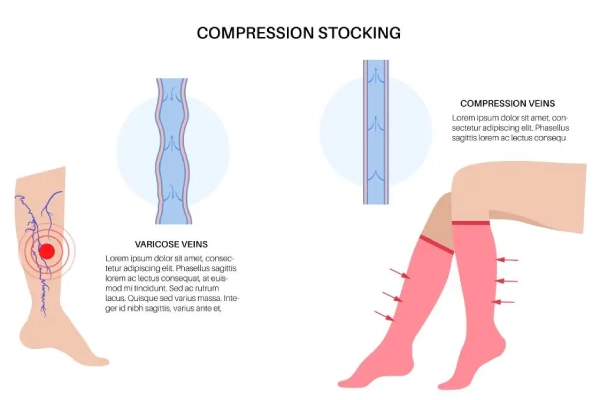
Graduated Compression Socks are the most common type, ideal for active people during daily activities or exercise. The pressure decreases from ankle to calf (typically 15-20 mmHg), making them suitable for everyday wear.
Anti-Embolism (TED) Socks target immobile patients on bed rest or recovering from surgery. They prevent blood clots in people who can’t move around regularly, using similar graduated pressure but designed for stationary use.
Support Socks provide lighter, uniform compression (8-15 mmHg) similar to athletic socks. While not medical-grade, they help with mild leg fatigue and are perfect for preventive care.
Who Needs Compression Socks and What Do They Do for Each Group?

Compression Socks for Travel and Long Flights
Extended sitting during flights creates ideal conditions for circulatory problems. Cabin pressure equivalent to 6,000-8,000 feet above sea level causes blood vessels to expand, while limited movement impairs natural circulation. Long-haul flights make deep vein thrombosis 1.5 to 4 times more likely.
Research shows compression stockings on flights over four hours significantly reduce both symptomatic and asymptomatic blood clot risk. The graduated pressure counteracts reduced cabin pressure effects and supports venous return despite challenging conditions. Travelers commonly report reduced ankle swelling and leg heaviness when wearing compression socks during and after flights.
Standing Jobs and Work Shifts With Compression Socks
Healthcare workers, retail employees, hairdressers, and servers face unique circulatory challenges from prolonged standing. Gravity continuously pulls blood downward while the absence of walking’s natural pumping action limits venous return, creating conditions for venous pooling.
Studies show compression therapy relieves varicose vein symptoms and edema in people with standing professions. The steady external pressure compensates for gravitational stress on vessel walls and valves, reducing fatigue and calf pain during long work shifts. Many hospitals now explicitly permit compression socks as part of uniform policies, recognizing their contribution to staff comfort.
Athletic Performance and Recovery
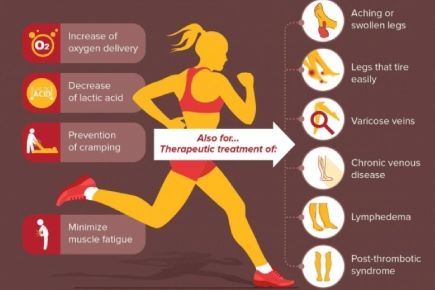
Athletes use compression socks for both performance enhancement and recovery acceleration. During activity, graduated pressure enhances venous return, improving oxygen delivery to working muscles while removing metabolic waste more efficiently. This can delay fatigue onset and maintain higher intensity for longer durations.
The structured support reduces muscle oscillation – micro-vibrations occurring on impact during running or jumping. By minimizing this vibration, compression socks help lower muscle fatigue and potentially reduce soft-tissue injury risk during prolonged activity.
Post-exercise, compression significantly reduces delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS) and accelerates strength recovery. Clinical studies show athletes wearing compression for 2-4 hours post-exercise experience fewer muscle damage biomarkers and report lower subjective soreness compared to control groups.
Compression Socks for Pregnants
Pregnancy creates unique circulatory challenges as blood volume increases by approximately 45% while elevated hormones cause vein walls to relax. The growing uterus exerts pressure on major veins, leading to fluid pooling in legs and ankles.
Clinical trials found pregnant women wearing compression stockings had significantly less leg swelling than those without them. The difference in calf and ankle diameter was dramatic by the end of pregnancy. Obstetricians often recommend 15-20 mmHg compression socks as safe, drug-free intervention for managing pregnancy-related edema, varicose veins, and leg heaviness.
Key Health Benefits of Compression Socks
Enhanced Circulation
Compression socks boost venous return through graduated pressure that mimics your body’s natural circulatory mechanics. This prevents blood pooling that causes swelling, heaviness, and discomfort while reducing cardiac workload and improving overall cardiovascular efficiency.
Reduced Swelling and Edema
The external pressure maintains proper tissue pressure gradients, preventing fluid leakage into surrounding tissues. Clinical studies consistently show compression stockings limit fluid buildup in legs, with users noticing less ankle and calf puffiness after long periods of sitting or standing.
Pain and Fatigue Relief
Graduated pressure reduces leg pain and uncomfortable sensations from poor circulation by supporting weakened vein walls and improving overall circulation efficiency. People with varicose veins experience particular relief, while healthy individuals report less tiredness and achiness throughout the day.
Muscle Recovery Support
For athletes and active individuals, compression improves muscle performance indicators and reduces exercise soreness. The enhanced circulation helps remove metabolic waste products more efficiently while maintaining muscle temperature, supporting faster recovery between training sessions.
Medical Therapeutic Benefits
In medical settings, compression therapy serves as primary treatment for chronic venous insufficiency, post-thrombotic syndrome, and lymphedema. The external support helps compensate for compromised venous function, reducing symptoms and potentially slowing disease progression.
Potential Side Effects and Important Considerations of Compression Socks
While compression stockings offer significant benefits, users should be aware of possible adverse effects. You may experience brief leg pain or discomfort after removing compression stockings, which occurs as blood vessels readjust to normal pressure levels. However, some individuals report prolonged discomfort, skin irritation, or circulation issues that can persist for extended periods. These problems may arise from improper sizing, wearing stockings for excessive durations, underlying circulation disorders, or individual sensitivity to compression materials. Additionally, poorly fitted compression wear can create pressure points, restrict movement, or even worsen circulation in some cases.
For a comprehensive examination of these potential complications, their underlying causes, and evidence-based prevention strategies, please review our specialized article addressing these concerns and choose the right compression level (15-20 mmHg / 20-30 mmHg). Understanding both benefits and risks, then wearing properly, ensures you can make informed decisions about incorporating compression therapy into your health routine.
Ready to create your own line of compression socks? We manufacture private label options with medical-grade quality, flexible MOQs, and fast lead times. Contact us now to discuss how we can help bring your compression sock brand to life.
FAQ
How long should I wear compression socks each day?
Wear them during active hours, typically 8-12 hours daily. Put them on in the morning before swelling starts and remove before bed unless medically advised otherwise.
Can compression socks be worn during exercise?
Yes, many athletes wear them during workouts for improved circulation and reduced muscle fatigue. They’re especially popular among runners for both performance and recovery benefits.
What compression level should I choose for everyday use?
Mild compression (15-20 mmHg) works for general daily wear, helping circulation and fatigue. Higher levels (20-30+ mmHg) require healthcare professional recommendation.
Are there any side effects to wearing compression socks?
Properly fitted compression socks are generally safe. Some may experience minor initial skin irritation. Overly tight socks can restrict rather than improve circulation.
How do I know if compression socks are working?
You should notice reduced swelling, less leg fatigue, and decreased achiness after long sitting or standing periods. Users typically report more leg energy and less heaviness.
