Introduction: The Growing Popularity of Compression Therapy
Expansion Beyond Medicine
Compression socks began as a tool for venous disease but have quickly moved into new arenas. Athletes lace up for perceived performance gains. Office workers and retail staff don them to combat leg fatigue. Frequent flyers pack a pair for long-haul comfort. Wellness brands market compression as everyday recovery. This trend reflects broader consumer interest in self-care gadgets that promise measurable benefits without drugs or invasive procedures.
Key Markets and Drivers
Four markets stand out: athletics, occupational health, travel, and general wellness. Sports teams cite studies suggesting faster recovery between workouts. Employers seek ways to boost on-the-job comfort and productivity among staff who stand or sit for hours. Airlines and travel brands promote them as a simple, portable defense against in-flight swelling and clot risk. Meanwhile, wellness influencers showcase compression socks as part of a daily ritual to “feel lighter” or reduce achiness. Each segment fuels greater product variety—from budget basics to high-tech, moisture-wicking models.
Core Questions on Efficacy
With so many use cases, a central question emerges: do compression socks actually deliver? Consumers want hard evidence that graduated pressure eases swelling, prevents clots, speeds recovery, or improves endurance. Marketing claims range from dramatic (“boosts performance by 15%”) to modest (“may help reduce mild edema”). Sorting fact from hype requires examining the underlying science, clinical trials, and real-world user reports. This guide tackles that task, weighing research quality, population differences, and practical considerations to help you decide if and when compression therapy earns a place in your routine.
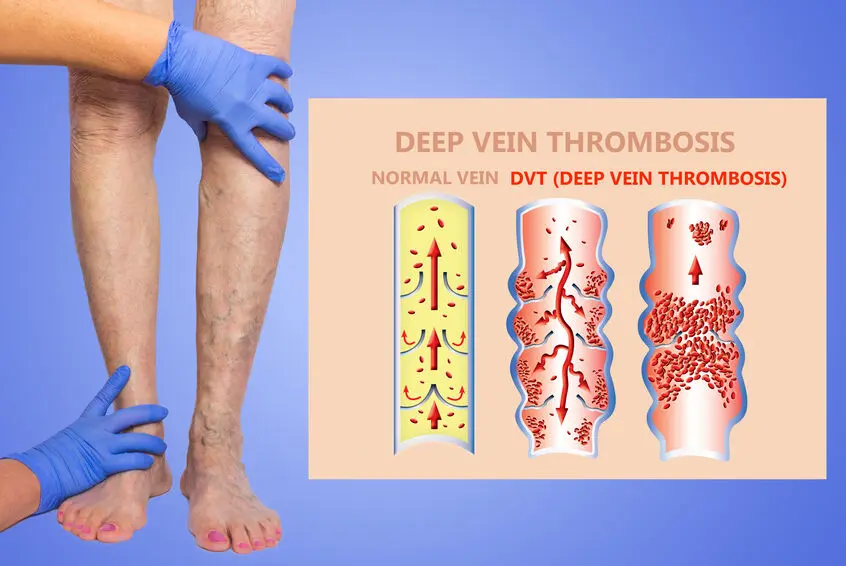
The Science Behind Compression: How Graduated Pressure Affects Circulation
Graduated Pressure and Venous Return
Graduated compression applies the highest pressure at the ankle, gradually lessening up the calf. This gradient assists the one-way valves in leg veins, preventing backflow and pooling. By mechanically supporting venous return, compression socks reduce the volume of blood that sits idle in the lower limbs. Improved venous return eases symptoms like heaviness and cramping and lowers the risk of clot formation in susceptible individuals.
Effects on Arterial Flow
While compression primarily targets veins, it can also influence arterial circulation. Mild external pressure may enhance the arteriovenous pressure differential, encouraging more consistent arterial inflow. Some studies demonstrate small but measurable increases in cutaneous blood perfusion under compression. However, excessive pressure risks impeding arterial supply, so understanding the optimal mmHg range is crucial to balance venous support without compromising arterial delivery.
Lymphatic and Fluid Dynamics
The lymphatic system removes excess interstitial fluid and waste from tissues. Graduated compression enhances lymphatic drainage by boosting the return of protein-rich fluid to the central circulation. This mechanism reduces tissue edema and may accelerate clearance of metabolic byproducts. Together with venous effects, improved lymph flow underpins much of the therapeutic rationale for compression in conditions like lymphedema and sports recovery.
Medical Evidence: What Research Says About Therapeutic Applications
Venous Insufficiency and DVT Prevention
A substantial body of clinical trials supports compression therapy for chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). Meta-analyses show that 20–30 mmHg socks reduce leg pain, swelling, and ulcer recurrence. In surgical and bedridden patients, thigh-high compression dramatically lowers deep vein thrombosis incidence by up to 60%. Consistency of findings across randomized controlled trials makes this one of the strongest medical use cases.
Lymphedema and Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
For lymphedema—persistent swelling from lymphatic damage—compression garments remain a mainstay. Studies report volume reductions of 30–50% when combined with manual drainage techniques. In post-thrombotic syndrome, graduated compression mitigates chronic leg pain and heaviness but shows mixed results on ulcer healing, suggesting individual factors like compliance and garment fit play critical roles.
Venous Ulcers and Wound Healing
Compression bandaging ranks as first-line therapy for venous ulcers, with healing rates nearly double those of no-compression controls. High-compression systems (40 mmHg at the ankle) achieve the most rapid wound closure. Yet patient adherence can suffer if garments are uncomfortable or difficult to apply, underscoring the need for user-friendly designs in clinical practice.
Athletic Performance: Can Compression Socks Improve Your Workout?
Endurance and Fatigue Resistance
Several trials measure time-to-exhaustion on treadmills or cycle ergometers with versus without compression. Results often show modest endurance gains (2–5%) and reduced perceived exertion, particularly in repeated-interval protocols. These effects appear more pronounced in recreational athletes than in well-trained elites, suggesting baseline fitness influences responsiveness.
Biomechanical and Power Effects
Compression can alter muscle oscillation and joint stiffness. Surface-EMG studies indicate reduced calf muscle vibration under load, potentially improving running economy. However, measurements of peak power output in sprint or jump tests generally show no substantial difference. The biomechanical benefits may favor endurance over explosive activities.
Statistical vs. Practical Significance
Even when data reach statistical significance, real-world impact matters. A 3% performance improvement may translate to seconds saved in a marathon but is negligible for most weekend athletes. Understanding the difference between “p < 0.05” in a lab and a perceptible edge in competition is key to deciding whether compression gear is a worthwhile addition to your training kit.
Recovery Benefits: Accelerating Post-Exercise Muscle Rehabilitation
Reducing Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness
After intense exercise, tiny muscle fibers experience microtrauma. This damage triggers inflammation and the familiar ache called delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS). Compression socks apply gentle pressure that limits muscle oscillation during and after activity. Studies show that athletes wearing compression gear report lower DOMS scores 24–72 hours post-exercise. The external support appears to reduce swelling within the muscle belly, minimizing discomfort during daily activities and follow-up training sessions.
Impact on Biomarkers of Muscle Damage
Muscle damage releases creatine kinase (CK) into the bloodstream. Elevated CK correlates with greater tissue breakdown. Research comparing CK levels in athletes wearing compression versus control groups finds up to a 20% smaller CK spike when compression is worn after exercise. This suggests that graduated pressure helps contain inflammation locally, slowing the diffusion of CK into circulation. While CK reduction does not guarantee faster strength recovery, it indicates less systemic stress after strenuous workouts.
Perceived Pain and Functional Recovery
Beyond biomarkers, perception matters. In randomized trials, participants rate their pain on visual analog scales while performing movements like squats or calf raises. Those using compression socks during the first 24 hours of recovery consistently report lower pain scores and less stiffness. Functional tests—such as vertical jump height or single-leg hop distance—also tend to return to baseline faster in compression groups. This combination of reduced soreness and maintained function lets athletes resume training sooner with lower injury risk.
Occupational Use: Evidence for Workplace Benefits
Alleviating Leg Fatigue and Discomfort
Workers who stand for long periods—retail associates, healthcare staff, factory operators—often end shifts with aching calves and heavy legs. Compression socks provide graduated support that counters blood pooling in the lower limbs. Clinical workplace studies reveal that employees wearing 15–20 mmHg socks report up to a 30% reduction in subjective fatigue scores at day’s end. This relief translates into less muscle soreness and a more comfortable commute home.
Reducing Swelling and Varicose Vein Risk
Prolonged standing or sitting can trigger fluid accumulation in ankles and feet. Compression garments limit edema by encouraging venous return and lymphatic drainage. In observational studies of flight attendants and nurses, regular use of compression socks cuts ankle circumference gains by half compared to no compression. Over years, consistent compression wear also correlates with lower incidence of new varicose veins, helping workers avoid long-term vascular complications.
Productivity and Absenteeism
Leg discomfort and swelling can distract employees and lead to break requests or early clock-outs. In one pilot study, a retail group provided compression socks saw a 15% drop in unscheduled breaks and a 10% reduction in absentee days attributed to musculoskeletal complaints. While more large-scale research is needed, early data suggest that compression therapy can boost on-the-job focus, morale, and overall productivity by reducing leg-related complaints.
Travel Applications: Do They Really Prevent Flight-Related Issues?
Preventing In-Flight Edema
Sitting immobile for hours—whether on a plane, train, or bus—slows venous return. Gravity and cabin pressure changes promote fluid leakage into surrounding tissues. Studies on long-haul travelers show that wearing 15–20 mmHg compression socks can halve the typical ankle swelling seen after flights over four hours. Travelers often note firmer, less puffy calves upon deplaning, making compression a simple tactic to maintain mobility and comfort on arrival.
Reducing DVT Risk in Air Travelers
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a rare but serious flight-related concern. Research in moderate-risk passengers indicates that thigh- or knee-high compression at 20–30 mmHg cuts DVT incidence by up to 75% compared to no compression. Airlines and travel medicine guidelines now endorse compression socks for individuals with risk factors—such as prior clot history, obesity, or recent surgery—particularly on journeys longer than six hours.
Enhancing Traveler Comfort and Well-Being
Beyond clinical outcomes, compression socks contribute to general comfort. Travelers report feeling less stiffness, faster recovery of normal gait, and reduced leg fatigue. In surveys, over 80% of compression users said they would pack them for future trips. The combination of measurable edema control and subjective comfort gains makes compression a valuable travel accessory for both business and leisure passengers.
Placebo Effect: Psychological Factors in Perceived Benefits
Expectation and Outcome
Belief in a treatment often shapes perception of its effectiveness. When users expect relief or performance gains from compression socks, they may focus more on positive sensations—like reduced heaviness or improved comfort—while overlooking minor discomforts. In double-blind studies where participants wear identical garments labeled as “therapeutic” or “placebo,” both groups frequently report similar levels of symptom improvement, highlighting expectation’s role.
The Role of Marketing and Branding
Product claims, celebrity endorsements, and premium pricing can amplify perceived benefits. Consumers tend to equate higher cost or scientific-sounding jargon with greater efficacy. Packaging that emphasizes “medical-grade” or “club-approved” compression may prime users to experience stronger effects. Awareness of these influences helps distinguish genuine physiological improvements from those driven by persuasive messaging.
Designing Better Trials
Reliable assessments must control for placebo responses. High-quality trials use sham compression—garments that look identical but apply negligible pressure—to compare against true compression socks. Measuring objective outcomes (e.g., blood flow via Doppler ultrasound) alongside subjective surveys allows researchers to separate real circulatory changes from psychological effects. Such rigorous designs yield clearer evidence regarding the true impact of graduated pressure.
Individual Variation: Why Results Differ Between Users
Anatomical and Physiological Differences
Leg shape, calf muscle mass, and vein valve competence vary widely across individuals. Graduated pressure that feels perfect for one person might leave another with inadequate support or unwanted tightness. Skin thickness and subcutaneous fat layers also influence how pressure is transmitted to underlying tissues. These anatomical factors explain why two users wearing the same mmHg rating can report divergent comfort and efficacy.
Activity Level and Lifestyle
A sedentary office worker and a marathon runner place very different demands on their legs. Compression socks interact with muscle contractions and movement patterns. Active users may benefit from enhanced proprioception and vibration damping, while less active individuals rely more on the garments’ resting pressure. Matching compression level and wear schedule to lifestyle—such as work hours or training sessions—optimizes outcomes for each user.
Fit, Compliance, and Donning Technique
Proper donning ensures graduated pressure works as intended. Socks that roll, wrinkle, or sag fail to maintain the pressure gradient, reducing effectiveness. Users with limited dexterity or poor instruction may apply garments incorrectly. Moreover, consistent daily use is critical: sporadic wear yields inconsistent benefits. Education on measuring, choosing the right size, and putting on compression correctly helps minimize variation in results.
Risk Factors: When Compression Socks Might Cause Harm
Arterial Insufficiency Concerns
Compression socks can further limit blood flow in individuals with peripheral arterial disease (PAD). Narrowed arteries already struggle to deliver sufficient oxygenated blood; added external pressure risks aggravating ischemia and pain. Signs like cold, pale feet or a low ankle-brachial index warrant medical evaluation before wearing compression hosiery.
Skin Integrity and Neuropathy
Fragile or compromised skin—due to stasis dermatitis, eczema, or recurrent cellulitis—can tear or ulcerate under compression. Similarly, those with sensory neuropathy (e.g., diabetic patients) may not notice excessive tightness, increasing risk of pressure sores. Contraindications include open wounds, infection, or hypersensitivity to sock materials. In such cases, medical-grade bandages or alternative therapies may be safer.
Improper Sizing and Application
Risks also arise when socks are too tight or applied unevenly. Excessive pressure at the cuff can create a tourniquet effect, causing a sharp indentation and restricting circulation distal to the band. Users should monitor for numbness, tingling, or persistent redness. If these symptoms appear, removing the socks and rechecking sizing or consulting a healthcare professional is essential to prevent harm.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Are Premium Products Worth the Investment?
Construction and Material Differences
Premium compression socks often feature higher-grade materials—like advanced microfiber blends or copper-infused yarns—and more precise knitting techniques that deliver consistent graduated pressure. They may incorporate reinforced heel/toe zones, seamless toes, and flatlock stitching to reduce irritation. While budget options cover basic graduated squeeze, premium lines typically last longer, feel softer against skin, and maintain their mmHg rating through more wash cycles.
Durability and Pressure Retention
Lower-cost socks can start losing effective compression after 20–30 washes, whereas high-end models often guarantee consistent pressure for 60–90 cycles. This translates to fewer replacements over time. If you wear compression daily, the cost of replacing budget socks every two months can match or exceed the one-time investment in a premium pair that lasts six months. Tracking wash count and pressure retention helps calculate real-world value.
Medical-Grade Certification vs. Retail Grade
Medical-grade compression garments undergo rigorous testing to verify their mmHg ratings, elasticity under stress, and safety standards. Retail-grade or “athleisure” compression may lack formal certification, meaning labeled pressure ranges could vary from actual performance. For therapeutic needs—like chronic venous insufficiency or DVT prevention—medical-grade certification provides assurance. Casual users focused on mild swelling or travel comfort may find retail-grade more cost-effective.
DIY Assessment: Determining If You’re a Good Candidate
Self-Screening Checklist
Start by listing your primary reasons: leg swelling, varicose veins, athletic recovery, or travel comfort. Note any risk factors such as a history of blood clots, diabetes, or peripheral arterial disease, which may require medical advice. Measure your ankle and calf circumferences and compare to sizing charts to see if you fit standard categories. If you hover between sizes or have unusual leg shapes, consider a trial pair before committing to multiples.
Trial and Observation
Purchase a single pair in the mmHg range suggested for your needs (15–20 mmHg for mild symptoms, 20–30 mmHg for moderate issues). Wear them during the activity in question—work shift, flight, workout—and keep a simple log of comfort levels, swelling measurements, and any sensations of numbness or tingling. After two weeks, review your notes: Has swelling decreased? Do your legs feel less fatigued? Is the fit comfortable throughout the day? This real-world test clarifies personal benefit.
When to Seek Professional Input
If you experience sudden or worsening leg pain, unusual skin changes, or signs of arterial insufficiency (cold feet, color changes), stop DIY use and consult a healthcare provider. A vascular specialist can perform an ankle-brachial index test or ultrasound to assess circulation and recommend a precise compression grade. For chronic conditions like lymphedema or severe varicose veins, professional fitting ensures therapeutic efficacy and safety.
Beyond Socks: Alternative Compression Options
Compression Sleeves and Stockings
For targeted support or easier application, calf compression sleeves focus pressure below the knee while leaving the foot free. Thigh-high stockings extend support further up the leg. Both styles use the same graduated principle but adapt to different needs—slip-on sleeves for quick relief or full stockings for comprehensive coverage. Stockings often include silicone bands at the top to prevent slipping.
Compression Leggings and Tights
Full-length compression tights combine abdominal support with graduated leg pressure, making them popular in pregnancy and postpartum recovery. Compression leggings—often worn during exercise—deliver consistent mmHg from ankle to waist. These garments integrate multiple support zones (calves, quads, hips) and sometimes pocket or waistband features for convenience.
Pneumatic Compression Devices
Medical-grade pneumatic systems use an air pump and inflatable sleeves to apply sequential compression. These devices mimic the graduated gradient but with adjustable pressure cycles and rest intervals. Often prescribed for severe lymphedema or post-surgical care, pneumatic pumps provide customizable therapy but require electricity or batteries, making them less portable.
Emerging Technologies
Innovations include smart compression wear embedded with sensors to monitor pressure and muscle activity in real time. Some experimental fabrics change compression dynamically in response to temperature or movement. While still in early stages, these technologies promise personalized, on-demand support that adapts to individual needs throughout the day.
Conclusion

Compression socks offer clear advantages for many users—from boosting venous return and reducing swelling to aiding recovery and preventing DVT on long flights. Yet individual factors like circulation health, fit accuracy, and intended use shape outcomes. Understanding the science, consulting evidence, and self-testing help ensure you reap genuine benefits without unintended harm.Whether you opt for athletic, medical-grade, or travel compression, start by identifying your primary need—performance, therapy, or comfort. Measure accurately, select the appropriate mmHg range, and trial a single pair to gauge real-world effects. If complex health issues arise, engage a healthcare professional to guide grade selection and fitting. A thoughtful approach transforms marketing claims into personalized, reliable support.
FAQ: Common Questions About Compression Sock Effectiveness
Do compression socks really prevent swelling?
Yes. Graduated pressure improves venous and lymphatic return, reducing fluid buildup in ankles and calves.
Can compression socks lower DVT risk on long flights?
For moderate-risk travelers, 20–30 mmHg socks cut DVT incidence by up to 75% when worn properly.
Will compression gear boost my athletic performance?
Evidence shows small endurance gains and reduced fatigue in recreational athletes, but elite benefits are modest.
Are higher-priced compression socks worth it?
Premium models retain pressure longer and feel more comfortable; budget pairs may need replacing twice as often.
How do I know if compression socks are unsafe for me?
Avoid compression with severe arterial disease, active leg infections, or sensory neuropathy—consult your doctor first.
