
Introduction
Swollen feet, puffy ankles, and bloated legs—these aren’t just minor inconveniences; they could be signs of a deeper issue. Edema, the medical term for fluid retention, affects millions of people worldwide, yet many remain unaware of its true causes. It’s easy to dismiss as a simple ache after a long day, but untreated edema can signal problems with your circulatory system, kidneys, or heart. So, what exactly is this condition, and why is it so widespread? In fact, certain groups are more prone to it than others—pregnant women, older adults, and those with a sedentary lifestyle are at a higher risk. But here’s the twist: while this condition is common, it doesn’t have to be a lifelong battle. Compression socks, a solution often overlooked, have been proven to manage and even reduce swelling. Intrigued?
Edema is swelling caused by fluid trapped in your tissues, often due to poor circulation, pregnancy, or prolonged sitting. Compression socks combat this by applying targeted pressure that gently squeezes your legs, assisting weak veins and pushing the stagnant fluid back towards your heart, effectively reducing swelling and relieving discomfort.
Let’s dive into what causes edema and explore how these specialized garments can provide lasting relief.
What Causes Edema?
Poor Circulation: When Your Blood Flow Needs a Boost
One of the most common causes of fluid retention is poor circulation. When blood struggles to travel efficiently through the veins, fluid can accumulate in the lower extremities. For those who sit or stand for long periods, the lack of proper blood flow can lead to swelling, particularly in the feet and ankles. Solutions often involve increasing physical activity or using support garments designed to encourage better circulation, helping to reduce the pooling effect of fluid in the tissues.
Hormonal Changes: How Hormones Can Affect Fluid Retention
Hormonal shifts play a significant role in fluid buildup. During pregnancy or certain phases of the menstrual cycle, the body produces hormones like progesterone, which can make blood vessels more permeable. This allows fluid to leak into surrounding tissues, resulting in temporary swelling. In addition, hormonal treatments, such as birth control or hormone replacement therapy, can lead to similar effects, affecting the body’s ability to regulate fluids properly.
Medications: Prescription Drugs That Can Lead to Swelling
Swelling can also be a side effect of certain medications, particularly those prescribed for high blood pressure, pain, and diabetes. Drugs like calcium channel blockers, corticosteroids, and NSAIDs can interfere with fluid regulation in the body, leading to excess fluid accumulation. If you notice unexpected swelling after starting a new medication, it’s essential to consult your healthcare provider to discuss alternatives or ways to manage this side effect.

Chronic Conditions: The Link Between Swelling and Heart, Kidney, and Liver Disease
Several chronic conditions are closely linked to fluid retention. Heart failure can impede the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively, causing fluid to accumulate in the legs and abdomen. Kidney disease can reduce the organ’s ability to filter excess fluids, while liver disease can affect protein production, disrupting fluid balance. Addressing these underlying conditions is critical to managing swelling and preventing its recurrence.
Pregnancy: Why Swelling is Common and What to Do About It
Swelling is a common and expected part of pregnancy, particularly in the later stages. The body produces extra blood and fluids to support the baby, and the growing uterus can exert pressure on veins, impeding circulation. This typically results in swelling in the feet, ankles, and legs. While this is usually harmless, lifestyle adjustments like keeping feet elevated, staying hydrated, and wearing supportive garments can help ease discomfort and manage swelling.
Lymphatic System Dysfunction: A Hidden Culprit
In some cases, edema stems from lymphatic system dysfunction, such as lymphadema, where the lymphatic vessels fail to drain fluid properly. This can occur due to injury, infection, or congenital abnormalities. Left untreated, lymphatic edema can lead to chronic swelling and tissue fibrosis.
Other Contributing Factors
- Skin Injury/Infection: Trauma or infections can damage capillaries, increasing permeability and fluid leakage.
- Ill-Fitting Footwear: Tight shoes can restrict circulation, particularly in the feet and ankles.
Signs and Symptoms: How to Identify Edema Early?
Recognizing Swelling in the Ankles, Legs, and Feet
The most obvious indicator of fluid retention is swelling, particularly in the lower legs, feet, and ankles. Early on, you might notice that your shoes feel tighter or that the affected areas look puffier than usual. This swelling can worsen as the day goes on, especially if you’ve been standing or sitting for extended periods. It can range from subtle to pronounced, and catching it early helps manage the condition before it becomes more difficult to treat.
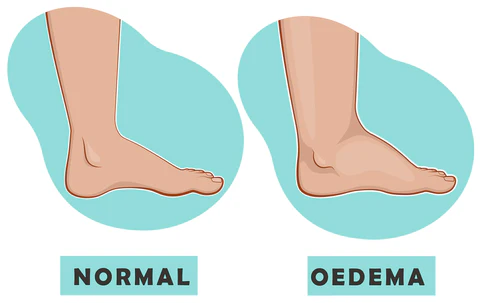
The Skin Test: How to Spot Pitting Swelling
To determine if you’re dealing with this condition, perform a simple skin test. Press your finger into the swollen area—if an indentation remains for a few seconds, you may have pitting swelling. This occurs when fluid moves under the skin, leaving a temporary depression. Pitting is a strong sign of fluid buildup and is typically linked to retention rather than other types of swelling, such as that caused by inflammation. This test can help assess the severity of the issue and decide whether you need medical attention or at-home care.
When Swelling Becomes Painful: Is It Time to Seek Help?
Mild swelling often isn’t serious, but when discomfort turns into pain, it may signal something more concerning. If swelling becomes tender, warm, or even red, it could point to an underlying problem like an infection or clot. Severe or persistent swelling that doesn’t improve with rest warrants a consultation with a doctor. Also, if you experience symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical care, as these could indicate serious health issues like heart failure or a blood clot.
How Edema Affects Your Health and Quality of Life?
Mobility Issues
When fluid builds up in the lower limbs, it often leads to discomfort and restricted movement. Swollen feet or legs can feel heavy and stiff, making simple activities like walking or climbing stairs difficult. Over time, this can severely limit one’s ability to perform daily tasks or maintain an active lifestyle. For individuals who rely on their mobility for work or exercise, this can be especially disruptive, affecting both personal and professional routines.
Risk of Skin Ulcers and Infections
Persistent swelling that remains untreated can lead to more serious issues, including the development of skin ulcers. These painful open sores are often a result of prolonged pressure from fluid accumulation and can become infected if not properly cared for. In addition, chronic swelling can make the skin more susceptible to cuts and abrasions, increasing the risk of further complications. Managing swelling early on is key to preventing these long-term health risks.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Constant swelling can also affect one’s emotional health. The physical discomfort and visible changes in appearance often lead to lowered self-esteem and frustration. This can be especially challenging for those who feel embarrassed or self-conscious about their condition. Over time, these feelings can contribute to stress, anxiety, or even depression, as individuals struggle to cope with the ongoing impact on their quality of life. It’s crucial to address not just the physical symptoms, but also the emotional toll of dealing with fluid retention.

The Benefits of Compression Socks for Edema
Relieve Swelling and Discomfort
Compression socks are designed to apply gentle pressure to the legs, which helps to promote blood flow and reduce fluid accumulation in the lower limbs. This targeted pressure alleviates the discomfort associated with swelling, such as tightness and heaviness in the legs. By supporting circulation, they effectively ease the discomfort and provide relief, allowing individuals to feel more comfortable throughout the day.
Prevent Fluid Build-Up
Consistent use of compression garments can have lasting effects in preventing fluid retention. By improving circulation, they help keep blood flowing efficiently, thus reducing the chances of fluid collecting in the legs and feet. Over time, regular wear can reduce the frequency and severity of swelling episodes, making it easier to manage the condition and maintain a more stable fluid balance. This makes them particularly beneficial for those who are prone to recurring swelling.
Enhance Lymphatic Drainage
Gradient compression socks also support the lymphatic system by encouraging the movement of excess fluid from tissues back into lymphatic vessels. This is especially critical for individuals with lymphatic edema, as it helps prevent fluid stagnation and reduces the risk of tissue fibrosis.
Aid in Athletic Recovery
Athletes often use compression socks to enhance performance and recovery. By improving blood flow, these garments reduce muscle fatigue, minimize lactic acid buildup, and speed up post-workout recovery.
Improve Mobility and Overall Comfort for Edema Sufferers
Wearing compression socks can significantly enhance mobility by reducing swelling and stiffness. The gentle pressure they provide helps keep the legs flexible, reducing the discomfort that can make walking or standing for long periods difficult. Individuals who rely on their physical mobility, such as those working in active jobs or participating in sports, often find that these garments support their movements, making daily activities more comfortable.
Enhancing Quality of Life
The benefits of compression socks extend beyond physical comfort—they can improve overall well-being. By addressing the symptoms of swelling and improving circulation, they help individuals engage in their daily activities without the burden of constant discomfort. For many, these garments provide emotional relief as well, reducing the visible signs of fluid buildup and boosting self-esteem. With better mobility and less physical strain, people can enjoy a more active, fulfilling lifestyle.
Types of Compression Stockings and Applicable People
Different Types of Compression Stockings
Compression stockings come in various forms, each designed for specific needs. Gradient compression stockings are the most common and provide higher pressure at the ankle that gradually decreases towards the knee or thigh. This pattern helps improve blood circulation, making them ideal for people who need to prevent swelling or improve circulation due to standing or sitting for long periods.
Anti-embolism stockings, on the other hand, are used primarily in medical settings to reduce the risk of blood clots in patients who are immobile or recovering from surgery. These socks apply a uniform pressure across the entire leg to maintain proper blood flow and prevent clot formation. Unlike gradient stockings, they do not have graduated pressure, making them suited to different medical needs.
Lymphedema Garments: Customizable for individuals with lymphatic edema, offering targeted compression and a tailored fit to avoid tourniquet effects.
Who Should Wear Compression Socks?
Compression garments are beneficial for a variety of individuals. Those with circulation issues, such as varicose veins or venous insufficiency, often rely on these stockings to alleviate swelling and improve blood flow. People who have a sedentary lifestyle or sit for extended hours—like office workers, frequent travelers, or truck drivers—can also benefit from regular use to reduce the risk of fluid buildup.
Pregnant women are another group that frequently experiences swelling in their legs and feet due to hormonal changes and fluid retention, making compression socks an effective solution. Athletes or people who engage in strenuous physical activities may use them to support muscle recovery and prevent soreness. Additionally, individuals post-surgery, particularly those with limited movement, may wear these garments to reduce swelling and the risk of blood clots.
Special Considerations for Diabetic Patients
Diabetic individuals should exercise caution when using compression socks, as neuropathy may mask discomfort or skin irritation. Opt for seamless, breathable designs and consult a healthcare provider to ensure proper fit.
Contraindications
Avoid compression socks if you have severe peripheral artery disease (PAD), as they may worsen ischemia.


When and How to Use Compression Socks Effectively?
When and How to Wear Compression Stockings?
For optimal results, it’s essential to wear compression garments at the right times. If you’re using them to prevent or manage swelling, it’s best to put them on first thing in the morning, before any fluid has accumulated. Wearing them throughout the day, especially during prolonged sitting or standing, will help maintain blood flow and prevent further fluid buildup. For individuals recovering from physical activity, wearing these socks immediately after exercise can help reduce muscle soreness by improving circulation.
For those experiencing pregnancy-related swelling, consistent use during the later stages of pregnancy can alleviate discomfort and prevent swelling from worsening. It’s important to ensure a proper fit to ensure the socks apply the right amount of pressure—snug but not tight, covering the necessary area to maximize circulation.
Tips for Proper Application
- Use a silicone-grip top to prevent rolling or bunching.
- Apply talcum powder to dry skin for easier sliding.
- Use a sock donner or rubber gloves for assistance if mobility is limited.
Maintenance and Replacement
- Wash socks regularly in mild detergent to preserve elasticity.
- Replace them every 3–6 months or when they lose compression.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Compression Socks
There are several common mistakes to be mindful of when using compression garments. One of the biggest errors is incorrect sizing. If the socks are too tight, they may cause discomfort or even restrict circulation, while if they’re too loose, they won’t provide adequate support. Always make sure to measure your legs accurately and select the appropriate size.
Another mistake is wearing these socks overnight. While they are meant for extended wear during the day, leaving them on while sleeping may not be necessary and could even cause discomfort. It’s generally best to remove them before bed to give your skin and circulation a break.
Lastly, poor maintenance of the socks can affect their performance. Regular washing is essential to maintain their elasticity and effectiveness. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for cleaning to ensure the socks remain in good condition and continue to provide the support needed.
Advice on Purchasing Compression Stockings
Compression Level
Choose a pressure level that matches your specific health needs. Lower compression levels (15–20 mmHg) are suitable for mild swelling, while higher levels (30–40 mmHg) are necessary for more severe conditions like lymphatic edema. For advanced cases, layered compression (e.g., 20–30 mmHg + 30–40 mmHg) may be recommended.
Material Quality
The material quality is another crucial factor. Look for stockings made of breathable, moisture-wicking fabrics like nylon or spandex, which prevent skin irritation and ensure comfort throughout the day. High-quality materials also contribute to the durability of the socks, ensuring they maintain their effectiveness over time.
Size
Size plays a vital role in the effectiveness of compression stockings. A perfect fit ensures that the pressure is evenly distributed without causing discomfort. Use a soft tape to measure ankle circumference, calf width, and leg length. And refer to the sizing guide provided by the manufacturer to select the correct size.
Style and Length
Style and length also vary based on personal preference and specific requirements. Compression socks come in various lengths, including knee-high, thigh-high, and full-length options. Choose a style that suits the areas you need support, whether it’s the ankles, calves, or thighs.
Professional Guidance
Before purchasing compression socks, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have a medical condition. A doctor or specialist can help determine the appropriate compression level and recommend the best type for your needs. In some cases, custom-made garments may be necessary to ensure an ideal fit, especially for those with chronic health conditions or specific treatment requirements.
Additionally, professional guidance can help ensure that compression socks don’t interfere with other treatments or exacerbate existing issues. Whether you’re using them for circulatory problems, recovery from surgery, or managing chronic swelling, seeking expert advice can help you make the best choice for your health.
Other Treatments for Edema: Can Compression Socks Be Enough?
Complementary Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
While compression garments are effective, they might not be the only solution for managing swelling. Incorporating lifestyle changes can greatly enhance the benefits of these stockings. Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to improve circulation and reduce fluid buildup. Gentle exercises, such as walking or cycling, encourage blood flow and help the body expel excess fluid naturally.
A healthy diet also plays a key role. Reducing sodium intake is crucial, as excess salt is a major contributor to water retention. Drinking plenty of water helps flush out the retained fluids, which can alleviate some of the swelling. Elevating the legs whenever possible helps fluid drain from the lower extremities, further reducing swelling. Simple practices like these can complement the benefits of wearing compression stockings.
In addition, some natural remedies such as dandelion or ginger can act as mild diuretics to encourage fluid loss. However, these should be used carefully and not as a replacement for more established methods of edema management.
Health Treatments and Prescriptions
For more severe cases, medical intervention may be required. Diuretics, commonly known as water pills, are often prescribed to reduce fluid retention. These medications help the body eliminate excess sodium and fluid, providing relief from swelling. However, they should only be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider, as improper use could lead to dehydration or other complications.
In addition to medication, treating the underlying condition responsible for the swelling—such as heart disease, kidney issues, or liver problems—is crucial. For instance, in individuals with heart failure, medications that improve heart function can reduce fluid accumulation. Similarly, those with kidney disease may need specialized treatments to address their condition and prevent excessive fluid retention.
For some individuals, manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) or physical therapy can also be beneficial. These therapies stimulate the lymphatic system and assist in fluid circulation, which can help prevent fluid buildup in the extremities.
Long-Term Management Strategies
- Weight Management: Excess weight increases venous pressure; maintaining a healthy weight can reduce swelling.
- Psychological Support: Chronic edema may impact mental health; consider counseling or support groups.
Conclusion
Edema can be an uncomfortable and often distressing condition, but understanding its causes and taking proactive steps to manage it can make a significant difference. Whether caused by poor circulation, hormonal changes, or underlying health conditions, the good news is that relief is possible. Compression socks provide a targeted and effective solution by promoting better circulation and reducing swelling. While these garments play a key role in managing edema, combining them with lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and medical treatments can lead to even greater improvement.
For brands and retailers looking to offer a customized solution to their customers, now is the perfect time to explore custom compression socks for your product lineup.
If you’re interested in providing your customers with effective, high-quality compression socks, get in touch with us to discuss how we can create a tailored compression sock solution for your brand.
FAQs
Q1. Are compression socks suitable for everyone with edema?
While compression socks can benefit many individuals with edema, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider to ensure they’re the right solution for your specific condition. In some cases, customized compression levels or alternative treatments may be necessary.
Q2. Can I use compression socks alongside other treatments for edema?
Yes! Compression socks are often most effective when combined with other treatments, such as medications, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes. A comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying cause of edema and promotes healthy circulation can lead to the best results.
Q3. How can I order custom compression socks for my brand?
If you’re a brand or retailer looking to offer custom compression socks, we can help! Reach out to us to discuss your specific needs, and we will work with you to create high-quality, tailored products that suit your customers’ needs. Contact us today to get started!
Q4. How long should I wear compression socks each day for edema relief?
The duration of wear depends on the severity of the edema and your healthcare provider’s recommendation. Generally, wearing compression socks for several hours a day—especially during activities that cause swelling, like standing or walking—can be highly beneficial. However, it’s important to follow your doctor’s guidance for personalized recommendations.
Q5. Can compression socks be worn while sleeping?
Generally, compression socks are designed for daytime wear, especially during periods of activity. However, depending on the severity of your edema and your doctor’s advice, wearing compression socks at night might be beneficial in certain cases. Always consult your healthcare provider before using them overnight.
Q6. Can compression socks be used as a preventive measure for edema?
Yes, wearing compression socks can be an effective preventive measure for individuals at risk of developing edema, especially those with poor circulation, standing jobs, or a history of swelling. They can help improve circulation and reduce the likelihood of fluid retention before it becomes a major issue.
